Modifications
KPVT (tank) is the current version of the basic design, used for vehicle installations and various AA mountings. It has a shortened receiver, which is a great bonus for guns that are mounted inside compact tank or APC turrets. KPVT also have heavier barrel jackets and use 50-round belts instead of the original 40-round ones. KPVT HMGs are the primary armament of the Soviet BTR-60B and BTR-70 armoured personnel carriers and BRDM armoured recon vehicles. The Type 56 (China) is a licensed copy of the KPV and the Type 75 (China) is a slightly modified KPV on improved AA mountings.
– – NSV NSVT- –
Caliber: 12.7×108
Weight: 25 kg (55 lbs) gun body + 16 kg (35 lbs) infantry tripod + 1.7 kg (3,7 lbs) SPP telescope sight
Overall length: 1,560 mm (61”) gun body
Barrel length: 1,346 mm (53”)
Cyclic rate of fire: 700 – 800 rpm
Feed and capacity: Belt, 50 rounds
The NSV heavy machine gun is a gas operated, air cooled, belt fed, automatic only, weapon which fires from an open bolt.
The gas system consists of a gas chamber, located below the barrel, with a gas regulator and a long-stroke gas piston attached to the bolt carrier. The barrel can be quickly replaced in the field during sustained fire. Field manuals recommend replacement of the barrel (or cease of fire for cooling) after 100 rounds fired in continuous burst(s). Each barrel is fitted with carrying handle. Once inserted into the receiver, the barrel is fixed in place with a locking wedge.
The receiver is of generally rectangular shape, and is assembled from heavy gauge steel stampings and machined inserts with many rivets. Bolt locking is achieved by lateral displacement of the entire bolt to the left side, until its locking lugs are engaged with locking recesses cut in the insert attached to the receiver wall. The bolt is linked to the bolt carrier with swinging links which control the longitudinal and lateral movement of the bolt and, once the bolt is in battery and fully locked, strikes the firing pin to discharge the gun. The bolt carrier has several anti-friction rollers which ride on the tracks cut in the receiver. The rear of the receiver houses a spring buffer for the bolt group.
The NSV uses non-disintegrating steel belts with open links; feed is of the single-stage type. Belts are assembled from 10-round pieces, using a cartridge as an interlink. Upon the indexing of the belt, the next fresh cartridge is pushed down from the belt pocket, by the dual delinking claws mounted in the feed unit, and put into the feed tray. During the forward movement of the bolt, the lug on the bolt strips the cartridge from the feed tray, forward and into the chamber. The standard belt feed unit feeds from the right side, but any NSV gun can be set up for alternative left-side feed. The belt indexing mechanism is built into the feed cover, which swings up and forward for loading and unloading. Spent cartridges are ejected forward through a short tube, located to the right of the barrel.
The firing mechanism of the NSV consists of a trigger lever with the necessary linkage to the sear, and a mechanical safety. Firing controls must be built into the mount, in the form of a pistol grip on the cradle of the infantry tripod, or a firing solenoid in the cradle of the tank mount.
The standard mounting is either an infantry tripod, adjustable for height and intended for ground fire only, or a low-profile AA mount with mechanical traverse and elevation mechanisms and special sighting equipment. The infantry tripod can be folded down and carried by the soldier as a backpack using special slings. This tripod also houses a foldable shoulder rest (with a spring recoil buffer), a pistol grip with trigger, and a gun charging mechanism. This consists of a steel cable with a T-grip, wound on a spring-loaded drum, with a gear and toothed rack that connects to the bolt carrier once the gun is properly installed on its cradle in the tripod.
In infantry configuration, two soldiers can move the NSV across the battlefield; the same two soldiers can carry the NSV for longer ranges if the gun is dismounted from the tripod. One soldier then carries the tripod as a backpack, while the other carries the gun body. Each man also carries one ammunition can with a belt.
Standard sighting equipment for infantry NSV guns is the SPP selectable power telescopic sight (3X or 6X), with an illuminated range-finding reticle. Each gun is also fitted with back-up iron sights, in the form of a hooded post front sight which is mounted on the barrel and folds down when not in use, and a tangent-type rear sight with a windage adjustment mechanism and a range scale marked from 400 to 2,000 m. The standard NSV crew is two men, the gunner and his assistant.
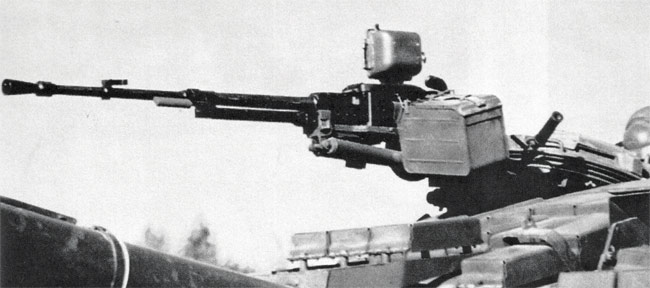
Modifications
NSVT (USSR / Russia; tank) is basically similar to the NSV except for the special mounting. NSVT machine guns are used mostly as roof-mounted AA / self-defense weapons on Soviet and Russian main battle tanks. The special tank mount has a buffered cradle, electrical (solenoid-operated) trigger, traverse and elevation mechanisms and a special collimating sight.
12.7mm MG-U (Bulgaria) – a straight copy of the original NSV weapon, available on a ground-use tripod or AA mount, both being copies of Soviet mounts.
– – Kord 6P50 – –
Caliber: 12.7×108 (also available in 12.7×99)
Weight: 25 kg (55 lbs) gun body + 16 kg (35 lbs) infantry tripod or 7 kg (15 lbs) lightweight bipod mount
Overall length: 1,980 mm (78”)
Cyclic rate of fire: 650-750 rpm
Feed and capacity: Belt, 50 rounds
The Kord HMG is a gas operated, air cooled, belt feed, automatic only, weapon. It uses a more or less conventional long stroke gas piston, located below the barrel, which is locked using a rotary bolt with multiple lugs. The barrel is quick-detachable and is fitted with highly effective muzzle brake. There are two basic patterns of muzzle brakes – early cylindrical one and current “flat” muzzle brake / flash hider.
The belt feed uses the same steel, non-disintegrating belts as the NSV. The standard feed direction is from the right, but the Kord can be set up to feed from the left if required. Spent cases are ejected forward through a short tube pinned to the right side of the receiver.
Like the NSV, the Kord has no firing controls on the gun body, other than a firing lever and mechanical safety. Actual fire controls and charging mechanisms, be that a manual trigger with pistol grip and manual charging handle, or an electric solenoid trigger and pneumatic or electrical charging system, are installed on the mount. The Kord retains the same mounting interface as the NSV, so it is used from the same infantry tripods, AA or tank mountings. Because of reduced recoil (compared with the NSV or other 12.7mm HMGs, thanks to the effective muzzle brake and buffers) the Kord is equipped with one rather unique mounting, which consists of a standard gun cradle of the NSV tripod (with pistol grip, charging mechanism and shoulder stock), with attached bipod legs.
The Kord has iron sights as standard (hooded front post and tangent rear), plus a special rail on the left side of receiver, which can accept mountings for variety of telescopic or infrared sights.